Blog News
The information provided on RenewMe Wellness is for educational and informational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health providers with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
Weight Management
The Impact of Weight Loss Medications on Metabolic Health
Introduction
Weight loss medications like semaglutide and tirzepatide are not only effective in promoting weight loss but also offer significant benefits for metabolic health. This article explores the impact of these medications on metabolic parameters such as insulin sensitivity, blood glucose levels, and lipid profiles.
Insulin Sensitivity
Both semaglutide and tirzepatide improve insulin sensitivity, which is crucial for individuals with type 2 diabetes. By enhancing the body’s response to insulin, these medications help lower blood glucose levels and reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications.
Blood Glucose Levels
Semaglutide and tirzepatide effectively lower blood glucose levels by increasing insulin secretion and decreasing glucagon release. This dual action helps maintain stable blood glucose levels, which is essential for metabolic health and preventing hyperglycemia.
Lipid Profiles
Weight loss medications can also positively impact lipid profiles. Studies have shown that both semaglutide and tirzepatide can reduce levels of LDL cholesterol and triglycerides while increasing HDL cholesterol. These changes contribute to improved cardiovascular health and reduced risk of heart disease.
Additional Metabolic Benefits
In addition to improving insulin sensitivity, blood glucose levels, and lipid profiles, these medications also help reduce inflammation and oxidative stress. This further enhances their benefits for overall metabolic health and supports long-term weight management.
Conclusion
Semaglutide and tirzepatide offer significant benefits for metabolic health beyond weight loss. By improving insulin sensitivity, stabilizing blood glucose levels, and enhancing lipid profiles, these medications contribute to better overall health and reduced risk of metabolic diseases. Patients should discuss these benefits with their healthcare providers to understand the full potential of their treatment.

Managing Side Effects of Semaglutide and Tirzepatide
Introduction
While semaglutide and tirzepatide are effective weight loss medications, they are not without side effects. Understanding and managing these side effects is crucial for maximizing the benefits of these treatments. This article discusses common side effects of semaglutide and tirzepatide and provides strategies for managing them.
Common Side Effects
Both semaglutide and tirzepatide are associated with gastrointestinal side effects such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. These side effects are usually mild and tend to subside as the body adjusts to the medication. However, they can be bothersome and may affect adherence to the treatment.
Managing Nausea and Vomiting
Nausea and vomiting are the most commonly reported side effects. To manage these symptoms, it is recommended to start with a low dose and gradually increase it as tolerated. Eating smaller, more frequent meals and avoiding high-fat or spicy foods can also help reduce nausea. Staying hydrated and taking the medication at bedtime may further alleviate symptoms.
Managing Diarrhea
Diarrhea can be managed by staying hydrated and consuming a balanced diet with adequate fiber. If diarrhea persists, over-the-counter medications may be used, but it is important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any additional treatments.
Long-term Management
Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are essential for monitoring side effects and making necessary adjustments to the treatment plan. Patients should report any persistent or severe side effects to their providers to ensure safe and effective use of the medications.
Conclusion
Managing the side effects of semaglutide and tirzepatide is crucial for ensuring their effectiveness in weight loss. By following recommended strategies and maintaining regular communication with healthcare providers, patients can minimize side effects and achieve their weight loss goals.
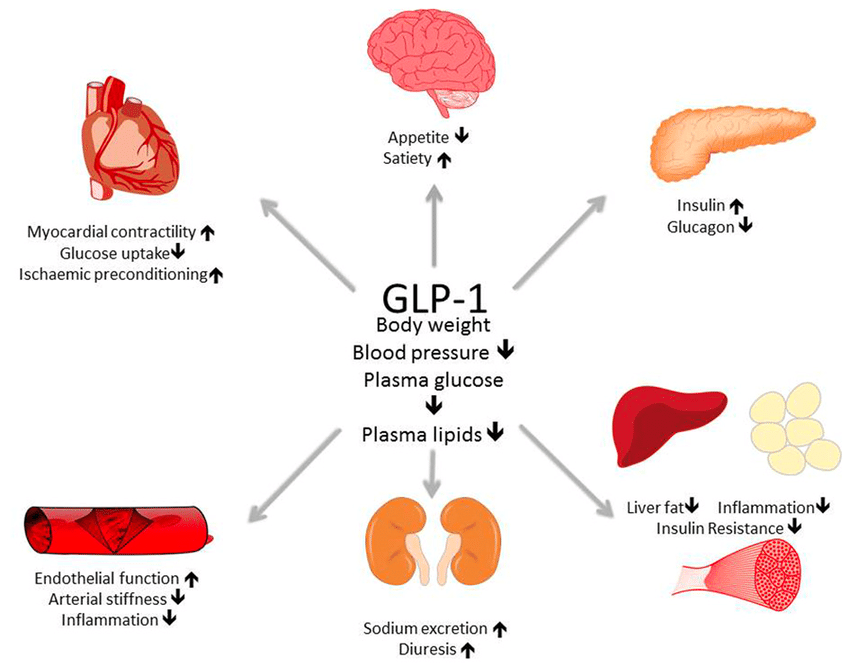
The Role of GLP-1 and GIP Receptors in Weight Management
Introduction
GLP-1 and GIP receptors are crucial targets in the treatment of obesity and type 2 diabetes. Medications like semaglutide and tirzepatide leverage these receptors to promote weight loss and improve metabolic health. This article explores the roles of GLP-1 and GIP receptors and how they contribute to weight management.
GLP-1 Receptors
GLP-1 receptors are primarily involved in regulating glucose metabolism and appetite. Activation of GLP-1 receptors enhances insulin secretion, decreases glucagon release, and slows gastric emptying, leading to reduced appetite and food intake. Medications like semaglutide, which are GLP-1 receptor agonists, mimic these effects, helping individuals achieve significant weight loss.
GIP Receptors
GIP receptors play a similar role in regulating insulin release and energy balance. By targeting GIP receptors, medications can enhance insulin sensitivity and promote energy expenditure. Tirzepatide, a dual-action medication, targets both GLP-1 and GIP receptors, providing a comprehensive approach to weight management.
Combined Effects
By targeting both GLP-1 and GIP receptors, tirzepatide offers enhanced benefits for weight loss and metabolic health. Clinical trials have demonstrated that tirzepatide leads to greater weight loss compared to single-action medications like semaglutide. This combined approach addresses multiple aspects of metabolic regulation, making it a powerful tool for weight management.
Conclusion
GLP-1 and GIP receptors are key players in the regulation of appetite, glucose metabolism, and energy balance. Medications that target these receptors, such as semaglutide and tirzepatide, offer effective solutions for weight management and metabolic health. Understanding the roles of these receptors can help in choosing the most appropriate treatment for individual needs.




